Introduction to Virtualization and guest VM setup
Introduction to Virtualization and guest VM setup Free Tutorial Download
1 Introduction to Virtualization
This Chapter provides introductory information on virtualization. It discusses why you would want to use virtualization, the technology provided, and features of Oracle VM. It contains the following sections:
1.1 What is Virtualization?
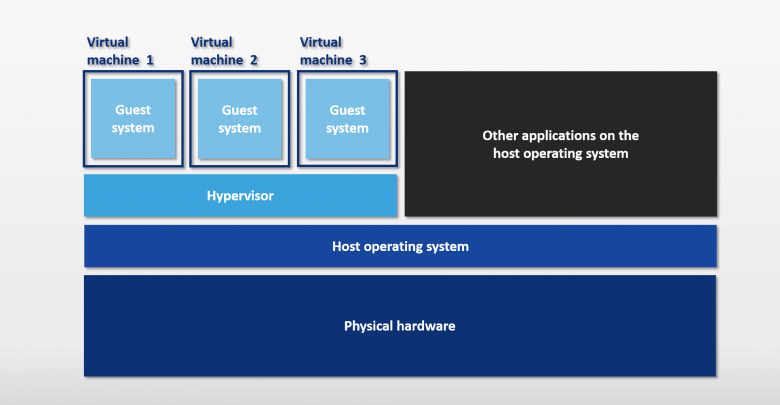
Virtualization is the ability to run multiple virtual machines on a single piece of hardware. The hardware runs software which enables you to install multiple operating systems which are able to run simultaneously and independently, in their own secure environment, with minimal reduction in performance. Each virtual machine has its own virtual CPU, network interfaces, storage and operating system.
1.2 Why Virtualize?
With increased server provisioning in the datacenter, several factors play a role in stifling growth. Increased power and cooling costs, physical space constraints, man power and interconnection complexity all contribute significantly to the cost and feasibility of continued expansion.
Commodity hardware manufacturers have begun to address some of these concerns by shifting their design goals. Rather than focus solely on raw gigahertz performance, manufacturers have enhanced the feature sets of CPUs and chip sets to include lower wattage CPUs, multiple cores per CPU die, advanced power management, and a range of virtualization features. By employing appropriate software to enable these features, several advantages are realized:
- Server Consolidation: By combining workloads from a number of physical hosts into a single host, a reduction in servers can be achieved and a corresponding decrease in interconnect hardware. Traditionally, these workloads would need to be specially crafted, partially isolated and well behaved, but with new virtualization techniques none of these requirements are necessary.
- Reduction of Complexity: Infrastructure costs are massively reduced by removing the need for physical hardware, and networking. Instead of having a large number of physical computers, all networked together, consuming power and administration costs, fewer computers can be used to achieve the same goal. Administration and physical setup is less time consuming and costly.
- Isolation: Virtual machines run in sand-boxed environments. Virtual machines cannot access the resources of other virtual machines. If one virtual machine performs poorly, or crashes, it does not affect any other virtual machine.
- Platform Uniformity: In a virtualized environment, a broad, heterogeneous array of hardware components is distilled into a uniform set of virtual devices presented to each guest operating system. This reduces the impact across the IT organization: from support, to documentation, to tools engineering.
- Legacy Support: With traditional bare-metal operating system installations, when the hardware vendor replaces a component of a system, the operating system vendor is required to make a corresponding change to enable the new hardware (for example, an Ethernet card). As an operating system ages, the operating system vendor may no longer provide hardware enabling updates. In a virtualized operating system, the hardware remains constant for as long as the virtual environment is in place, regardless of any changes occurring in the real hardware, including full replacement.
1.3 Xen™ Technology
The Xen hypervisor is a small, lightweight, software virtual machine monitor, for x86-compatible computers. The Xen hypervisor securely executes multiple virtual machines on one physical system. Each virtual machine has its own guest operating system with almost native performance. The Xen hypervisor was originally created by researchers at Cambridge University, and derived from work done on the Linux kernel.
The Xen hypervisor has been improved and included with Oracle VM Server.
1.4 Oracle VM
Oracle VM is a platform that provides a fully equipped environment for better leveraging the benefits of virtualization technology. Oracle VM enables you to deploy operating systems and application software within a supported virtualization environment. The components of Oracle VM are:
-
Oracle VM Manager: Provides the user interface, which is a standard ADF (Application Development Framework) web application, to manage Oracle VM Servers, virtual machines, and resources. Use Oracle VM Manager to:
- Create virtual machines
- Create server pools
- Power on and off virtual machines
- Pause and unpause live virtual machines
- Deploy virtual machines
- Manage virtual NICs (Network Interface Cards), disks and shared disks
- Create virtual machine templates from virtual machines
- Import virtual machines and templates
- Manage high availability of Oracle VM Servers, server pools, and guest virtual machines
- Perform live migration of virtual machines
- Import and manage ISOs
- Oracle VM Server: A self-contained virtualization environment designed to provide a lightweight, secure, server-based platform for running virtual machines. Oracle VM Server is based upon an updated version of the underlying Xen hypervisor technology, and includes Oracle VM Agent.
- Oracle VM Agent: Installed with Oracle VM Server. Oracle VM Manager communicates with Oracle VM Agent to manage the Oracle VM Servers and virtual machines running on it.
Download Introduction to Virtualization and guest VM setup Free
https://xmbaylorschool-my.sharepoint.com/:u:/g/personal/grayem_baylorschool_org/EWQ6omPUxq9JplZfqUKcFIYBalr1CollNgaEzoQKq9a8XA
https://bayfiles.com/l7scpbUfoe
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1B-EAs99AbwZT4SmmvpHsZb8QbpFKNalR/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/14NGyKPXrn37AlgjdVEl5I13D5_J62-tI/view?usp=sharing
https://uptobox.com/p5f8rrgwck7c



